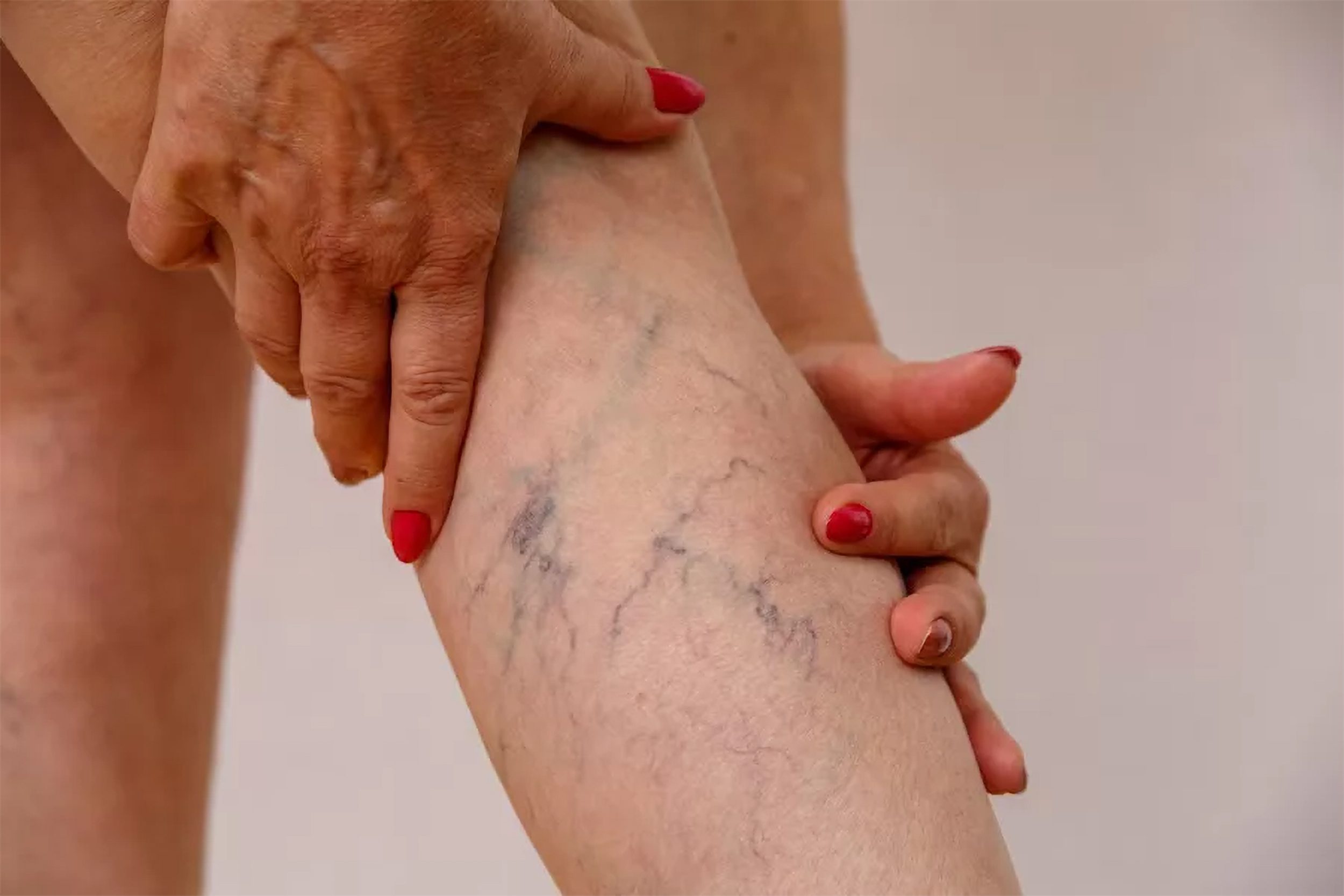
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition during which a blood clot (thrombus) occurs in a deep vein, usually located within the legs. If left untreated, it may lead to some very serious complications, including pulmonary embolism (PE), when a clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs. Early diagnosis and treatment are of utmost importance to avoid the potentially fatal consequences.
With SurgiKure, now we can easily find the best, most experienced vascular surgeons who treat deep vein thrombosis (DVT) cases in Visakhapatnam and other big cities under the most advanced, medically accepted techniques.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is the formation of a blood clot in one of the deep veins, which is normally located in the leg. The disease can be serious. This is especially so if the clot has dislodged and become lodged in the lungs, which could result in a fatal pulmonary embolism. Fortunately, appropriate care and safety measures can avert and treat DVT almost entirely. In this blog, we will discuss the ways of minimizing your changes of getting DVT and treatments. If you have already received the diagnosis with Deep Vein Thrombosis.
Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Certain factors increase the chance of DVTs. Among them are the following common risk factors:
- Prolonged immobilization: seating or lying down for a significant amount of time, such as with a long flight or being in bed after surgery. This can slow down blood circulation and it may increase the chances of developing clots.
- Age: It is probable to people aged 60 years and older because their blood circulation is slowed, among other causes. old-age related.
- Medical conditions: These include heart disease, obesity, cancer, and autoimmune diseases.It can increase your chance of developing blood clots.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy increase blood clotting factors, making DVT more prevalent in pregnant women.
- Hormone therapy or birth control pills: Some forms of hormonal birth control, such as childbirth, can increase your risk of blood clots.
- Family history: A family history of DVT or a blood clotting disorder may increase your risk of blood clots.
- Injury or surgery: Damage to blood vessels due to injury or surgery could lead to an increase in the incidence of deep vein thrombosis.
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) symptoms may be variable, and some may not notice something has gone wrong. Common symptoms include:
- Swelling in one leg, typically in the calf or thigh.
- Pain or tenderness in the calf and thigh.
- Redness or discoloration of the skin above the affected area.
- The skin around the clot may feel warmer than the surrounding areas.
- Swollen, firm, or visible veins may form on the skin’s surface.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Sudden shortness of breath.
- Sharp chest pain or discomfort that worsens with deep breaths.
- Rapid heartbeat or dizziness.
- Coughing blood.
How to Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Prevention is the best approach when it comes to Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment (DVT). Here are some strategies you can use to reduce your risk:
- Exercise regularly: Walking, cycling, and swimming are great ways to get your blood flowing.
Move often On a long trip: If you’re traveling by plane, train, or car, take a break every hour to stand. Stretch and walk around for long trips. - Avoid sitting still for too long: If you work at a desk or watch TV for long periods of time, take a short break to stretch and move around.
- Wear compression socks: Compression socks are specifically designed to apply gentle pressure to your feet. It helps blood flow better and helps reduce blood clots, it is especially useful for people who are unable to move or sit for long periods of time, such as during long-haul flights or hospital stays.
- Keep your body hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help prevent dehydration. Drinking water consistently will thicken your blood and raise your risk of blood clots.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight or obese may raise your chance of developing DVT owing to increased pressure and changes in blood flow in your veins.Eating a balanced diet combined with regular exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce your risk of blood clots.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the chance of blockages. If you are a smoker, quitting smoking can reduce your risk of DVT.
Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep Vein Thrombosis is diagnosed through a combination of clinical examination, risk assessment, and diagnostic tests:
-
The Wells Score measures the possibility of DVT based on symptoms and risk factors.
-
D-Dimer Test: A blood test used to determine clotting activity; increased values indicate the existence of a clot.
-
Doppler Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging diagnostic that detects the presence of a clot.
-
Other imaging options include venography, CT, or MRI for more complicated instances or pelvic vein clots
Treatment Procedure of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Doctors determine whether Standard or Advanced methods should be used to treat Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) treatment based on clinical observation and diagnostic test results.
Treatment will aim to reduce the development of clot, decrease the chances of a complication, and avoid the formation of new clots.
Standard Method of Treatments
Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners):
- Apixaban and Rivaroxaban are DOACs (Direct Oral Anticoagulants)
- Heparin is an unfractionated or low molecular weight
- Warfarin (Coumadin) is monitored with INR
Compression stockings:To prevent swelling and post-thrombotic syndrome.
Advanced Method of Treatments
- Thrombolysis: Catheter-directed thrombolytic therapy for large DVT.
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: The physical removal of a clot.
- IVC Filters: These are devices inserted to stop blood clots from traveling and reaching the lungs if the use of anticoagulants is not possible.
Conclusion
Of course, recognizing the risk factors and taking care of oneself to maintain healthy circulation is the best way to prevent and treat Deep Vein Thrombosis. From staying active, wearing compression stockings, managing obesity or smoking, to a myriad of other methods, there are many ways to reduce the chances of having a DVT. Prompt medical treatment can prevent severe complications and significantly improve outcomes if diagnosed.