Introduction
Hysterectomy is a major surgery that alters a woman’s reproductive system and often requires the removal of the uterus. While it can be beneficial in the treatment of many illnesses, it has side effects, such as the patient being unable to conceive and facial hair growth. This guide aims to include information on the various forms of hysterectomy, conditions women might be at risk of having the surgery done to them, and how the process can be done.
This blog is for anyone who wants to know more about this Hysterectomy treatment and is thinking about hysterectomy or already decided to undergo this operation, You will be able to find out more about the hysterectomy treatment here: Hysterectomy treatment options; The fundamentals: Different types of hysterectomy surgeries; Common medical conditions that may require hysterectomy; The procedure and pre-operative preparation; Recovery and post-operative care: Hysterectomy treatment options with Surgikure.

What is a hysterectomy?
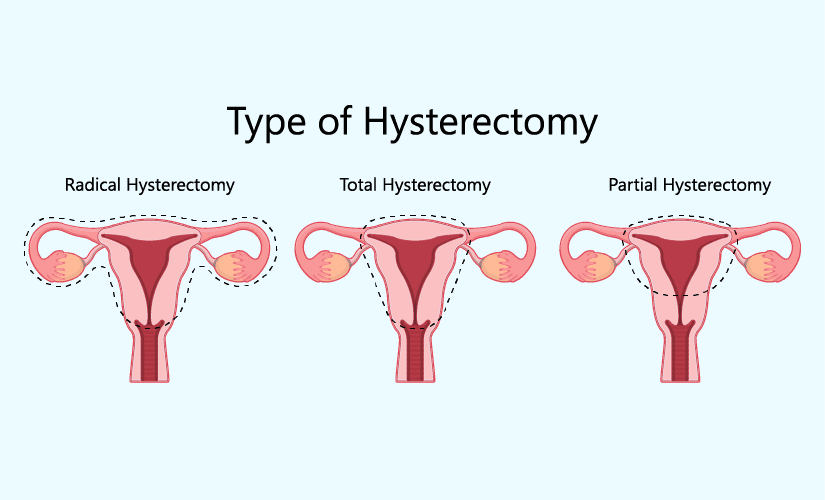
A hysterectomy can be defined as the surgical elimination of the uterus and health status, for instance, the fallopian tubes and the ovaries. This surgery is appropriate for women experiencing complications such as fibroids, endometriosis, or cancer illnesses. There are three main types of hysterectomy, each serving different medical needs:
- Total Hysterectomy: This includes the complete surgical operation to also remove the cervix in addition to the uterus.
- Supracervical Hysterectomy: Endometrial cryoablation: only the upper area of the uterus is removed but the cervix is not removed.
- Radical Hysterectomy: This is usually done for cancer and entails the surgical excision of the uterus and adjoining structures. Examples of this are the upper part of the vagina, the Fallopian tubes, the adjoining tissue, and the pelvic lymph nodes.
After a hysterectomy has been performed, a woman stops menstruating and is no longer capable of conceiving. It’s essential for women considering this surgery to have detailed discussions with their healthcare providers to weigh the pros and cons, especially if they are of childbearing age.
Why is a Hysterectomy performed?
Most hysterectomies are done when there is a disease cause that affects a woman’s fertility. Some of the most common reasons include:
1. Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids are benign tumors of smooth muscles that occur in the uterus. It is one of the many causes of hysterectomy that may be so common among women of childbearing age. In some cases, fibroids cause significant effects, including massive vaginal bleeding, pain, and discomfort in the pelvic region. Although medication or other forms of treatment such as endoscopic surgery, laparoscopic surgery, and laser surgery, which are minimally invasive surgeries, may control fibroid growth, a hysterectomy is done when non-surgical treatments do not work or when fibroids re-emerge.
2. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where endometrial tissue builds outside the uterus; causes severe pain, painful periods, and may affect fertility. Laparoscopic surgery is somewhat less invasive than open surgery and may be tried first to treat endometriosis, along with hormonal therapies that can be administered for initial treatment of the disorder. However, in the case where a woman develops chronic symptoms that cannot be relieved with these treatments, a hysterectomy might be performed to arrest the pain.
3. Uterine or Cervical Cancer
It is customary to perform a hysterectomy first in case of a uterine, ovarian, or cervical cancer diagnosis in women. The idea is to enable the surgeon to excise the organs that he thinks might be affected by cancer in order to stop its spread. In particular, if the cancer has not spread, surgery may help to remove the uterus and save the woman’s life. Mentioned above, surgery is usually accompanied by chemotherapy and radiation as other treatments.
Other Conditions
Other reasons for a hysterectomy may include:
- Certain forms of chronic pelvic pain, such as those that do not respond to other forms of therapy.
- Where the uterus slips to the vaginal canal, this is called uterine prolapse.
- Potentially life- threatening and a situation that cannot be handled without adverse effects on the patient’s health.

Preparing for a Hysterectomy Treatment
The following are the things that are undertaken to prepare for a hysterectomy in order to ensure that the process and after process are as comfortable as possible. Here are some things to keep in mind:
- Pre-operative Assessments: Most doctors who are planning to carry out the surgery will first make sure that they have to assess your general health. This may entail a simple blood test, an x-ray or CAT scan, and a physical pelvic examination. The aim of all the procedures performed is to make sure that the patient’s health is optimized in readiness for the procedure.
Questions to ask your Doctor: And before a hysterectomy, one should know of the surgery and the potential consequences it is bound to have. Some questions you may want to ask include:
- When it comes to hysterectomy, what is the best surgery for me?
- For how many hours is the surgery going to take or can it be completed within a day and what is the basic procedure in the process of recovery?.
- What might go wrong?
- Will I be required to undergo hormone therapy after the surgery?
2. Anesthesia and Pain Management: The majority of hysterectomies are usually done under general anaesthesia. As with many surgeries, the type of hysterectomy required may vary based upon the patient’s medical condition and therefore the options for post-operative pain control may be different.
What to expect during and after the procedure
The hysterectomy procedure itself typically takes around one to four hours, depending on the complexity of the surgery. Your surgeon will use either an open surgical method, where an incision is made in the abdomen, or a minimally invasive technique, such as laparoscopy.
Post-operative Care and Recovery
- It should also be noted that hysterectomy as a surgical process takes one-four hours, depending on the case. Your surgeon, for the surgery, will employ the open approach where the surgeon makes an incision into the abdomen or a laparoscopic procedure.
- What has to be done as a patient after an operation has been performed?
- Recovery Timeline: Following the surgery, most women do not require a lengthy stay in the ward, as most of them are usually admitted for not more than four days. Recovery may be complete in about 4-6 weeks, depending on the type of surgery and physical condition of the patient.
- Managing post-operative symptoms: Some of the measures that a patient should take during the recovery period are to avoid lifting heavy objects, take some time off from work and let your doctor give you more instructions on your recovery period. Some mild soreness, tenderness, and radiation of pain is normal in the first 48 to 72 hours following the surgery along the area where sutures are placed.
- Emotional and Physical Impact: Women are often philosophical after hysterectomy, and they may feel relieved, sad, or anxious. Mental state alterations and, particularly, fluctuations in mood and energy level may have hormonal origins due to the removal of ovaries. As these changes are inevitable, it is wise to discuss with your surgeon the kind of support you will need after surgery.
The impact of a Hysterectomy on quality of life
Millions of women feel good after a hysterectomy because the operation cures them of severe pain, excessive bleeding, and other symptoms caused by fibroids or endometriosis. But there are also longer impacts, especially in the sphere of reproductive health, of the surgery. Menstruation stops after a hysterectomy, and if you have your ovaries removed, you will go through menopause at that specific time.
Sexual health and hormonal changes: most women get worried about their ability to maintain sexual health and hormonal changes after the surgery. Hysterectomy does not impact sexual functioning; however, a change of sexual desire or dryness of the vaginal part may be observed. These symptoms may be treated using hormone replacement therapy, although medical advice should be sought for this.
Conclusion
A hysterectomy is a serious surgery but for most women, this surgery can be a blessing in modifying painful or potentially deadly diseases. The principle to be followed here is that you need to know what choices are available to you and their implications. Welcome to Surgikure, where your health is of utmost importance to us as we ensure that we offer you excellent surgery services, accuracy, and individualized programs throughout your surgery journey. Be it the case of uterine fibroids, cancer, or any other condition, Surgikure provides the competent advice required in finding the right care.
To move forward and explore the options available to you, contact Surgikure now for a consultation.
FAQs
- What is a hysterectomy?
Hysterectomy is the removal of all or part of a woman’s uterus, at times accompanied by removal of the cervix, fallopian tubes, or ovaries. Periods or the ability to get pregnant will be gone after the surgery as well.
- In what situations does a woman need a hysterectomy?
Some reasons are a benign tumour (fibroids), endometriosis (a condition in which endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus), uterine prolapse, abnormal uterine bleeding, and cancer. Your doctor will prescribe it depending on your health situation.
- What is the recovery period after hysterectomy?
Recovery normally goes on for 4 to 6 weeks based on the type of surgery. In this case, there are lots of things that you can do that will have an impact on how fast you will be able to recover from surgery. These include adhering to the doctor’s recommendations on what to do after the surgery.
- Will I experience menopause after a hysterectomy?
If your ovaries are removed during the surgery, you will experience menopause right afterward. If not, you may still possibly experience menopause the natural way at some point in your life.
