Hemorrhoids or commonly called piles are swollen porous veins located in the lower rectum and the anus area. They may lead to discomfort, pain and even bleeding which has an impact on the life of millions of people. However, the condition is mostly not life-threatening, yet it may greatly affect a person’s lifestyle. The following is a complete guide to hemorrhoids treatments, causes, symptoms, classification and diagnosis.
For Free Consultation : +91 7670968977
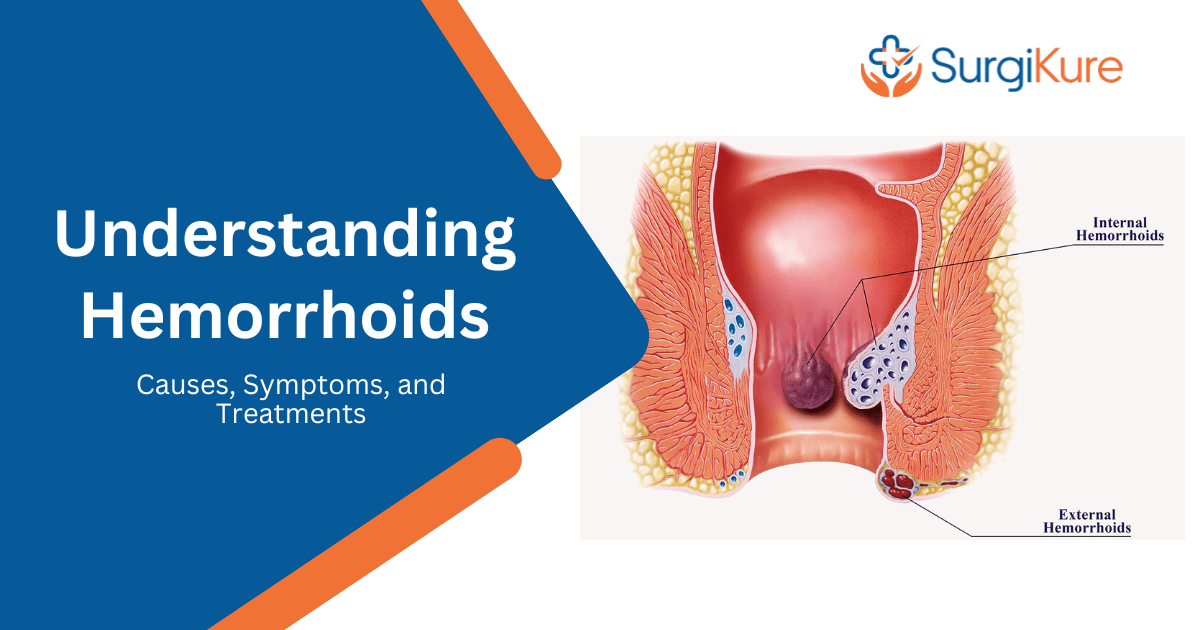
What are Hemorrhoids?
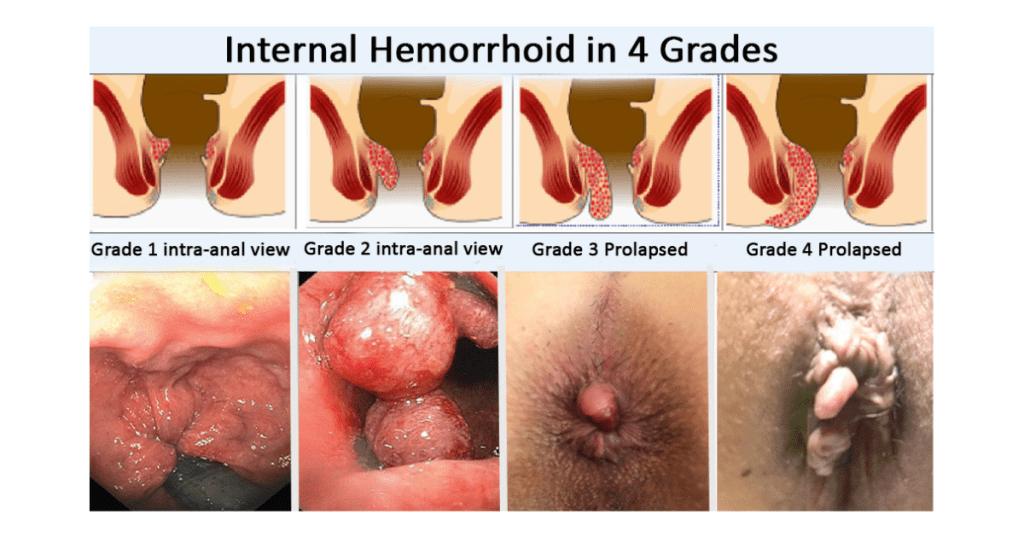
Hemorrhoids are simply swollen blood vessels that develop in the rectum and anus as a result of pressure build up. They can, however, be either primary, they originate on the inner walls of the rectum, or secondary which arise beneath the skin surrounding the anus. Hemorrhoids can be classified into four grades:
- Grade I: Inflammation or small lumps that are not surface but rather located in the inner surface of the anal canal.
- Grade II: Bigger sizes of Grade I hemorrhoids but they are likely to extend outside the anus (prolapsed hemorrhoids) during defecation and return to their place on their own.
- Grade III: Hemorrhoids that protrude, but cannot be manually reduced and involves one or more circles around the anus.
- Grade IV: Prolapsing hemorrhoids that are fairly big, that cannot be manually reduced and may necessitate an operation.
Causes of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids occur when the blood vessels near the lower rectum or the anus are stretched and get irritated easily when pressured. Several factors contribute to the development of hemorrhoids:
- Chronic Constipation: If one pushes during the bowel movements then the pressure exerted on the veins within the rectum and anus causes hemorrhoids.
- Diarrhea: That is, often defecation can also lead to pathological irritation and inflammation of the anal veins.
- Pregnancy: The expanding uterus also puts pressure on the veins in the rectum thus culminating into development of hemorrhoids during pregnancy.
- Obesity: Obesity puts pressure on the rectal veins and this results in formation of hemorrhoids.
- Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Sitting for long periods results in pressure build up in the rectal area and hence one should not sit for long.
- Low-Fiber Diet: Diet with Low fiber content may cause constipation and straining that poses a threat of piles.
- Aging: As one age, the anchoring tissues that hold the blood vessels underlying the rectum and anus can degenerate resulting in hemorrhoids.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can cause a range of symptoms, which vary depending on their type and severity:
- Painless Bleeding: Bright red blood may be observed on toilet paper or in the toilet after a bowel movement.
- Itching or Irritation: Skin around anus may develop itching or redness of the skin.
- Pain or Discomfort: This type of hemorrhoids can therefore cause various symptoms including pain and swelling especially when defecating.
- Swelling Around the Anus: This means that lumps which may sometimes be described as swelling at the anal region may be arising from external hemorrhoids.
- Mucus Discharge: Some people may experience mucus production after they have defecated and this is perfectly normal.
- A Feeling of Incomplete Evacuation: After defecation there may be a feeling that the colon is not empty.
Hemorrhoids Treatment
Currently anyone who has the symptoms of hemorrhoids should seek medical help for diagnosis. The diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical Examination: An assessment or inspection of the perianal area as a way of looking for the external hemorrhoids.
- Digital Rectal Exam: A doctor may anesthetize the area before putting a gloved finger that is lubricated into the rectum to check for hemorrhoids.
- Anoscopy: There is a hollow, lighted tube used in examining the anus to determine the presence of internal hemorrhoids.
- Sigmoidoscopy or Colonoscopy: Sometimes other conditions for example colorectal cancer should be ruled out by carrying out further tests.
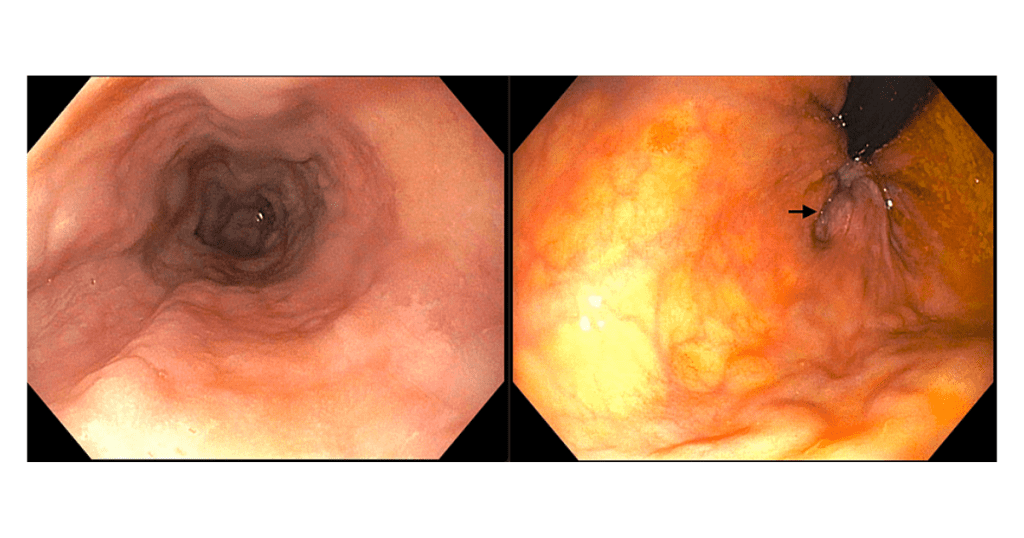

Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids
The management of hemorrhoids depends on the stage, and the signs manifesting. Some of the things one can do to manage their ailment include; diet modification, use of herbs, use of drugs, minimally invasive procedures and surgery.
- Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies:
- Dietary Changes: It is also advisable to increase intake of fiber content, especially from fruits, vegetables and whole grain products, since this will help them redue on straining.
- Hydration: One should drink a lot of water so as to ensure that free bowel movement is achieved.
- Regular Exercise: Exercise plays an important role in helping the body to prevent occurrence of constipation and hemorrhoid conditions.
- Avoid Straining: Do not force yourself when having bowel movements because this will put pressure on the anal veins.
- Warm Sitz Baths: Thus, warm water bath of the anal area for 10-15 min several times a day can effectively reduce the intensity of pain.
- Medications:
- Over-the-Counter Creams and Ointments: Anti-itch creams which may contain hydrocortisone or witch hazel can be used to alleviate the itching and relieve discomfort.
- Pain Relievers: For general soreness and oral pains you might use acetaminophen or ibuprofen to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Stool Softeners: Laxatives may be prescribed to a patient to help him/her ease the pressure and get soft stools instead of straining.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Rubber Band Ligation: A thin elastic band is slipped around the base of an internal hemorrhoid so that it becomes isolated and is starved of its supply of blood and thus shrinks and drops off.
- Sclerotherapy: The doctor puts a chemical solution that causes the shrinkage of the hemorrhoid.
- Infrared Coagulation: A special device is then applied to build scar tissue and therefore block the blood supply to hemorrhoid.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Hemorrhoidectomy is performed when the hemorrhoids are big or severe and other methods do not produce the desired result.
- Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: In this particular surgery, the surgeon uses a stapler to bring the prolapsed hemorrhoidal tissue back into the proper position and retains blood flow, which makes it shrink.
- Surgical Treatments:
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Hemorrhoidectomy is the most efficient way of treating hemorrhoids that are severe or those that tend to recur. It entails stripping of the swollen veins and can be done under local or general anaesthesia. Hemorrhoidectomy is a permanent surgical treatment for hemorrhoids and outcome may involve severe pain during the recovery period.
- Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: A procedure in which the hemorrhoid is simply relocated and its blood circulation is constricted. It is also important to note that this procedure is not as painful as the hemorrhoidectomy and has shorter recovery time.


Prevention of Hemorrhoids
Preventing hemorrhoids involves adopting healthy habits that reduce the risk of constipation and straining:
- Mainly get your foods rich in fiber, plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Make sure to take lots of water daily in order to increased the intake of water in your body.
- Stay active so as to maintain peristalism.
- Do not sit or stand for a long time, at least take a walk for some time, then come back to sit or stand again.
- Take a bath urgently when the urge of defecation arises so that you do not hold it up for very long.
Conclusion
Hemorrhoids are a quite usual ailment which a lot of people can face at various times in their life. Knowledge of the symptoms, causes and available cure for the condition can assist in living with the condition and perhaps minimize the effect. However, if the symptoms do not fade after some weeks or the pain is severe, one should seek the help of a doctor. At Surgikure, a comprehensive range of treatment options is available for hemorrhoids, including minimally invasive procedures like rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, and advanced surgical interventions. Through making some changes in one’s diet, taking appropriate drugs or even going through some operations, one can overcome this problem and have a good quality of life.
Useful links :